Dostęp do tego artykułu jest płatny.
Zapraszamy do zakupu!
Po dokonaniu zakupu artykuł w postaci pliku PDF prześlemy bezpośrednio pod twój adres e-mail.
REPORTAŻ KLINICZNY
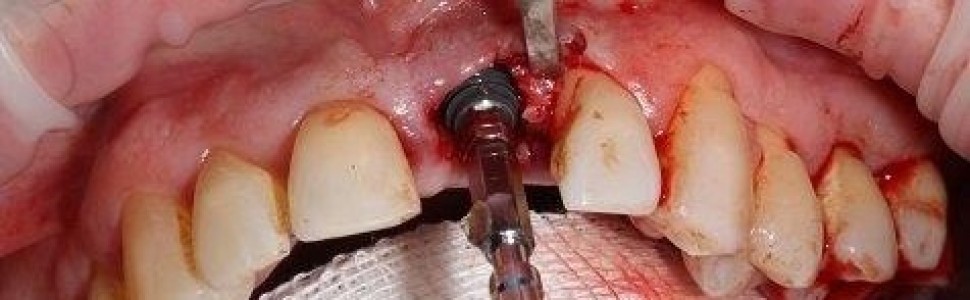
Implantacja natychmiastowa po minimalnie inwazyjnej ekstrakcji zęba – opis przypadku
Immediate implantation after minimally invasive tooth extraction. A case report
Aleksandra Urbanek-Wajda
Streszczenie
Złamanie korzenia zęba, zwłaszcza zęba siecznego przyśrodkowego szczęki, jest jedną z częstszych przyczyn zgłaszania się pacjentów na wizytę w trybie nagłym i pilnym do gabinetu stomatologicznego. Wymaga od lekarza protetyka wdrożenia kompleksowego i wielospecjalistycznego planu leczenia. Postępowanie terapeutyczne i rokowanie jest uzależnione głównie od przebiegu linii złamania i czasu, który upłynął od urazu, oraz właściwego zaopatrzenia przez lekarza udzielającego pacjentowi pomocy doraźnej. Opisany w artykule przypadek prezentuje metodę implantacji natychmiastowej, poprzedzonej minimalnie inwazyjną ekstrakcją zęba.
Abstract
Fracture of a tooth root, especially of the maxillary central incisor, is one of the most common reasons why patients make an emergency or urgent visit to a dentist’s office. It requires the prosthodontist to implement a comprehensive and multidisciplinary treatment plan. Therapeutic treatment and prognosis depend mainly on the course of the fracture line and the time that has passed since the injury, as well as the appropriate treatment provided by the doctor providing emergency treatment to the patient. The case described in the article presents a method of immediate implantation preceded by minimally invasive tooth extraction.
Hasła indeksowe: złamanie korzenia zęba, implantacja natychmiastowa, minimalnie inwazyjna ekstrakcja
Key words: tooth root fracture, immediate implantation, minimally invasive extraction
Piśmiennictwo
- Ryu HS, Namgung C, Lee JH. The influence of thread geometry on implant osseointegration under immediate loading. A literature review. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014; 6(6): 547-554.
- Atieh MA, Atieh AH, Payne AG i wsp. Immediate loading with single implant crowns. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Prosthodont. 2009; 22(4): 378-387.
- Glauser R, Zembic A, Hämmerle CH. A systematic review of marginal soft tissue at implants subjected to immediate loading or immediate restoration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17 Suppl 2: 82-92.
- McAllister BS, Cherry JE, Kolinski ML i wsp. Two-year evaluation of a variable-thread tapered implant in extraction sites with immediate temporization. A multicenter clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27(3): 611-618.
- Arnhart C, Kielbassa AM, Martinez-de Fuentes R i wsp. Comparison of variable-thread tapered implant designs to a standard tapered implant design after immediate loading. A 3-year multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2012; 5(2): 123-136.
- Orsini E, Giavaresi G, Trirè A i wsp. Dental implant thread pitch and its influence on the osseointegration process. An in vivo comparison study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27(2): 383-392.
- Grad P, Paruzel-Pliskowska A, Żegleń A i wsp. Przegląd wybranych atraumatycznych metod ekstrakcji. Nowa Stomatol. 2019; 24(3): 95-99.
- Cheah CW, Al-Namnam NM, Lau MN i wsp. Synthetic material for bone, periodontal, and dental tissue regeneration. Where are we now, and where are we heading next. Materials (Basel). 2021; 14(20): 6123.
- Ruales-Carrera E, Pauletto P, Apaza-Bedoya K i wsp. Peri-implant tissue management after immediate implant placement using a customized healing abutment. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2019; 31(6): 533-541.