Dostęp do tego artykułu jest płatny.
Zapraszamy do zakupu!
Po dokonaniu zakupu artykuł w postaci pliku PDF prześlemy bezpośrednio pod twój adres e-mail.
ARTYKUŁ Z FILMEM
Jednowizytowe leczenie endodontyczne zębów 32 i 31 z przewlekłym zapaleniem tkanek okołowierzchołkowych. Opis przypadku
Single visit endodontic treatment of teeth 32 and 31 with chronic periapical lesions. A case report
Jakub Barański, Natalia Stefanik, Krzysztof Kaźmierczak, Łukasz Wieczorek, Zofia Stefanik, Dariusz Skaba
Streszczenie
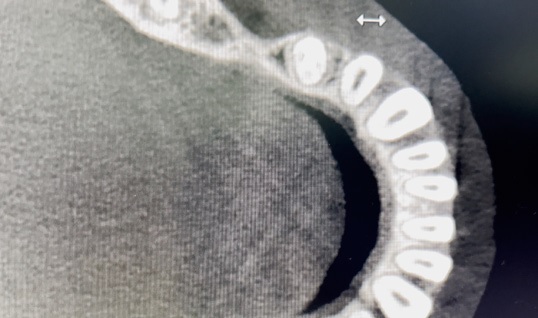
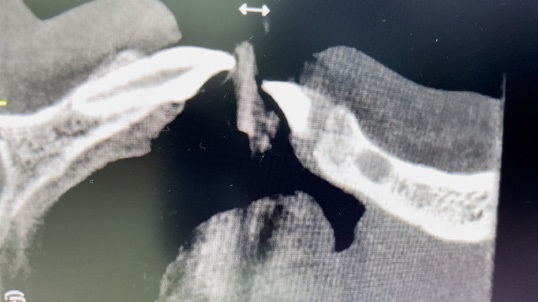
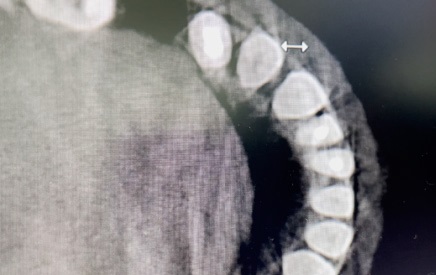
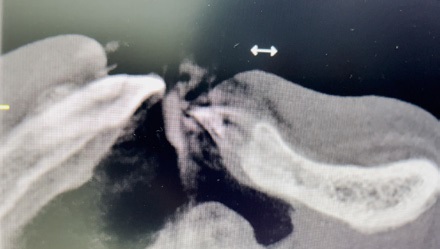
Diagnostyka przy użyciu tomografii komputerowej, leczenie w powiększeniu przy zastosowaniu mikroskopu zabiegowego, wsparcie laserowe poprzez fotobiomodulację celem zmniejszenia dolegliwości bólowych i przyspieszenia gojenia – to jedno z wielu udoskonaleń technologicznych, jakie w znaczący sposób przyczyniają się do sukcesu terapeutycznego. Prezentowany w artykule opis przypadku dotyczy 37-letniej pacjentki, która zgłosiła się z bólem w obrębie zębów 32 i 31. Tomografia komputerowa z wiązką stożkową (CBCT) ujawniła rozległe zmiany zapalne w tkankach okołowierzchołkowych z utratą blaszki przedsionkowej kości żuchwy przy zębach 32 i 31. Po szczegółowej diagnostyce podjęto decyzję o przeprowadzeniu leczenia endodontycznego podczas jednej wizyty. Zastosowano opracowanie chemo-mechaniczne kanałów przy użyciu narzędzi maszynowych Reciproc oraz obfitą irygację z użyciem 5,25% NaOCl, 40% kwasu cytrynowego, 0,9% NaCl. Obturację kanałów wykonano za pomocą kondensacji pionowej gutaperki na ciepło z użyciem uszczelniacza AH Plus. Celem polepszenia samopoczucia pacjentki i rokowań pozabiegowych przeprowadzono fotobiomodulację laserową, wykorzystując laser SMARTMPRO. Po 8 miesiącach kontrolne CBCT wykazało niemal całkowite wygojenie się zmian.
Abstract
Cone Beam Computed Tomography diagnostics, magnification treatment using a surgical microscope, laser support through photobiomodulation to reduce pain and accelerate healing – these are just one of many technological improvements that significantly contribute to therapeutic success. The case report concerns a 37-year-old female patient who presented with pain in the area of teeth 32 and 31. The CBCT showed extensive periapical changes with loss of the vestibular bone of the mandibula at the abovementioned teeth. After detailed diagnostics, it was decided to carry out endodontic treatment during one visit. The chemo-mechanical treatment of the canals was applied using Reciproc machine tools and abundant irrigation with the use of 5.25% NaOCl, 40% citric acid and 0.9% NaCl. The obstruction of the canals was done by warm vertical condensation of gutta-percha and by using AH Plus sealant. In order to improve the patient’s well-being and postoperative prognosis, laser photobiomodulation was performed using the SMARTMPRO laser. After 8 months, the control CBCT showed almost complete healing of the lesions.
Hasła indeksowe: leczenie endodontyczne, leczenie jednowizytowe, laser diodowy, tomografia komputerowa z wiązką stożkową
Key words: endodontic treatment, single visit treatment, diode laser, cone beam computed tomography
Piśmiennictwo
- Ikram O, Neal T, Mounce R. Endodontics: single versus multiple visit. International Dentistry – African Edition. 2021; 11(5): 26-33.
- Almeida DO, Chaves SC, Souza RA i wsp. Outcome of single- vs multiple-visit endodontic therapy of nonvital teeth. A meta-analysis. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2017; 18(4): 330-336.
- Schwendicke F, Göstemeyer G. Single-visit or multiple-visit root canal treatment. Systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017; 7(2): e013115.
- Manfredi M, Figini L, Gagliani M i wsp. Single versus multiple visits for endodontic treatment of permanent teeth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; 12(12): CD005296.
- Madurantakam P. Are single-visit regenerative endodontic procedures successful in treating non-vital, immature young permanent teeth? Evid Based Dent. 2020; 21(4): 136-137.
- Mohmmed SA, Vianna ME, Penny MR i wsp. The effect of sodium hypochlorite concentration and irrigation needle extension on biofilm removal from a simulated root canal model. Aust Endod J. 2017; 43(3): 102-109.
- Kandaswamy D, Venkateshbabu N. Root canal irrigants. J Conserv Dent. 2010; 13(4): 256-264.
- Dioguardi M, Gioia GD, Illuzzi G i wsp. Endodontic irrigants. Different methods to improve efficacy and related problems. Eur J Dent. 2018; 12(3): 459-466.
- Antony DP, Thomas T, Nivedhitha MS. Two-dimensional periapical, panoramic radiography versus three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography in the detection of periapical lesion after endodontic treatment. A systematic review. Cureus. 2020; 12(4): e7736.
- Sisli SN, Gulen O. Root canal length measurement of molar teeth using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Comparison of two-dimensional versus three-dimensional methods. Eur Oral Res. 2021; 55(2): 94-98.
- Das UK, Das S. Dental operating microscope in endodontics – a review. J Dent Med Sci. 2013; 5(6): 1-8.
- Selvakumar G, Mavishna M. Magnification in endodontics! Essential or Gimmick? J Dent Med Sci. 2021; 20(7): 46-55.
- Babtan AM, Ilea A, Feurdean CN i wsp. Biostimulation with low-level laser therapy and its effects on soft and hard tissue regeneration. Literature review. J Mind Med Sci. 2022; 9(1): 28-37.
- Shah D, Ponappa MC, Ponnappa KC. Evaluation of effect of low level laser therapy with intracanal medicament on periapical healing. A randomised control trial. Indian J Dent Res. 2021; 32(3): 299-304.
- Doğanay Yıldız E, Arslan H. Effect of low-level laser therapy on postoperative pain in molars with symptomatic apical periodontitis. A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Endod. 2018; 44(11): 1610-1615.
- Khalighi HR, Anbari F, Beygom Taheri J i wsp. Effect of low-power laser on treatment of orofacial pain. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2010; 4(3): 75-78.
- Lopes LPB, Herkrath FJ, Vianna ECB i wsp. Effect of photobiomodulation therapy on postoperative pain after endodontic treatment. A randomized, controlled, clinical study. Clin Oral Investig. 2019; 23(1): 285-292.
- Nabi S, Amin K, Masoodi A i wsp. Effect of preoperative ibuprofen in controlling postendodontic pain with and without low-level laser therapy in single visit endodontics. A randomized clinical study. Indian J Dent Res. 2018; 29(1): 46-50.
- Singh A, Konark, Kumar A, i wsp. Incidence of postoperative flare-ups after single-visit and multiple-visit endodontic therapy in permanent teeth. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2020; 38(1): 79-83.
- Erdem Hepsenoglu Y, Eyuboglu TF, Özcan M. Postoperative pain intensity after single- versus two-visit nonsurgical endodontic retreatment. A randomized clinical trial. J Endod. 2018; 44(9): 1339-1346.
- Gupta NK, Mantri SP, Paul B i wsp. Incidence of postoperative pain after single-visit and multiple-visit root canal therapy. A randomized controlled trial. J Conserv Dent. 2021; 24(4): 348-353.
- Shresha R, Shrestha D, Kayastha R. Post-operative pain and associated factors in patients undergoing single visit root canal treatment on teeth with vital pulp. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2018; 16(62): 220-223.
- Nagendrababu V, Gutmann JL. Factors associated with postobturation pain following single-visit nonsurgical root canal treatment. A systematic review. Quintessence Int. 2017; 48(3): 193-208.